STEMCELL Technologies STEMdiff STEMdiff Megakaryocyte Kit
- 研究用
- 新製品
STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit(ST-100-0900)は、ヒトの胚性幹(ES)細胞および人工多能性幹(iPS)細胞から巨核球および血小板に分化させる培地です。無血清かつフィーダーフリーの条件下で、血小板放出能を有しCD41aおよびCD42bを発現する倍数体巨核球に分化させることができます。
簡易な2次元培養による17日間の分化プロトコルを次の2段階で実施します。第一段階(12日間)では、STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic Supplement A、次いでSupplement MK1を基礎培地に添加し、細胞を巨核球分化傾向をもつ造血前駆細胞に誘導します。第一段階終了時に、培養上清から造血前駆細胞を簡単に回収できます。これを第二段階(5日間)でさらに、Supplement MK2とStemSpan™ SFEM IIを用いて成熟巨核球に分化させます。
分化プロトコルの終了時(17日目)に、細胞は通常405 ± 54倍(95% CI)まで増幅し、平均71 ± 3.3%(95% CI)がCD41aおよびCD42bを共発現します。
本品は、mTeSR™1(ST-85850)、mTeSR™ Plus(ST-100-0276)、またはTeSR™-AOF(ST-100-0401)で維持したヒトES/iPS細胞(hPSC)の分化に最適です。
製品の特長
STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kitで、hPSCから巨核球と血小板に分化
- 血清・フィーダー不使用
- hPSCのインプットあたり高収量の巨核球を産生
- 血小板放出能のある高倍数性の巨核球を取得
- フィーダーフリーで大量培養にも適合
巨核球分化のプロトコル
Figure 1. Megakaryocyte Differentiation Protocol
The 17-day protocol includes two main stages: a 12-day stage to differentiate human embryonic stem (hES) or induced pluripotent stem (hiPS) cells into megakaryocyte-biased hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs), and a 5-day stage to further differentiate hES or hiPS cell-derived HPCs into mature megakaryocytes (MKs). On Day -1, hES or hiPS cells are plated as aggregates (100 - 200 μm diameter, ~100 cells per aggregate) at a density of 10 ‑ 20 aggregates/cm2 in mTeSR™1, mTeSR™ Plus, or TeSR™-AOF on Corning® Matrigel®-coated plates. After attaching overnight and confirming the number of adhered colonies is within 4 - 10 colonies/cm2, mesoderm induction is initiated by replacing TeSR™ medium with Medium A (STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic Basal Medium + STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic Supplement A). On Day 3, the medium is changed to Medium MK1 (STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic Basal Medium + STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Supplement MK1) for endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition (EHT) and hematopoietic specification. During this phase, hES or hiPS cell-derived HPCs emerge from an adherent layer of endothelial cells and are released into suspension. On Day 12, HPCs in suspension are harvested and replated in Medium MK2 (StemSpan™ SFEM II + STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Supplement MK2) at a density of 1 - 3.5 x 105 cells/mL and cultured for 5 days to generate mature MKs.
データ紹介
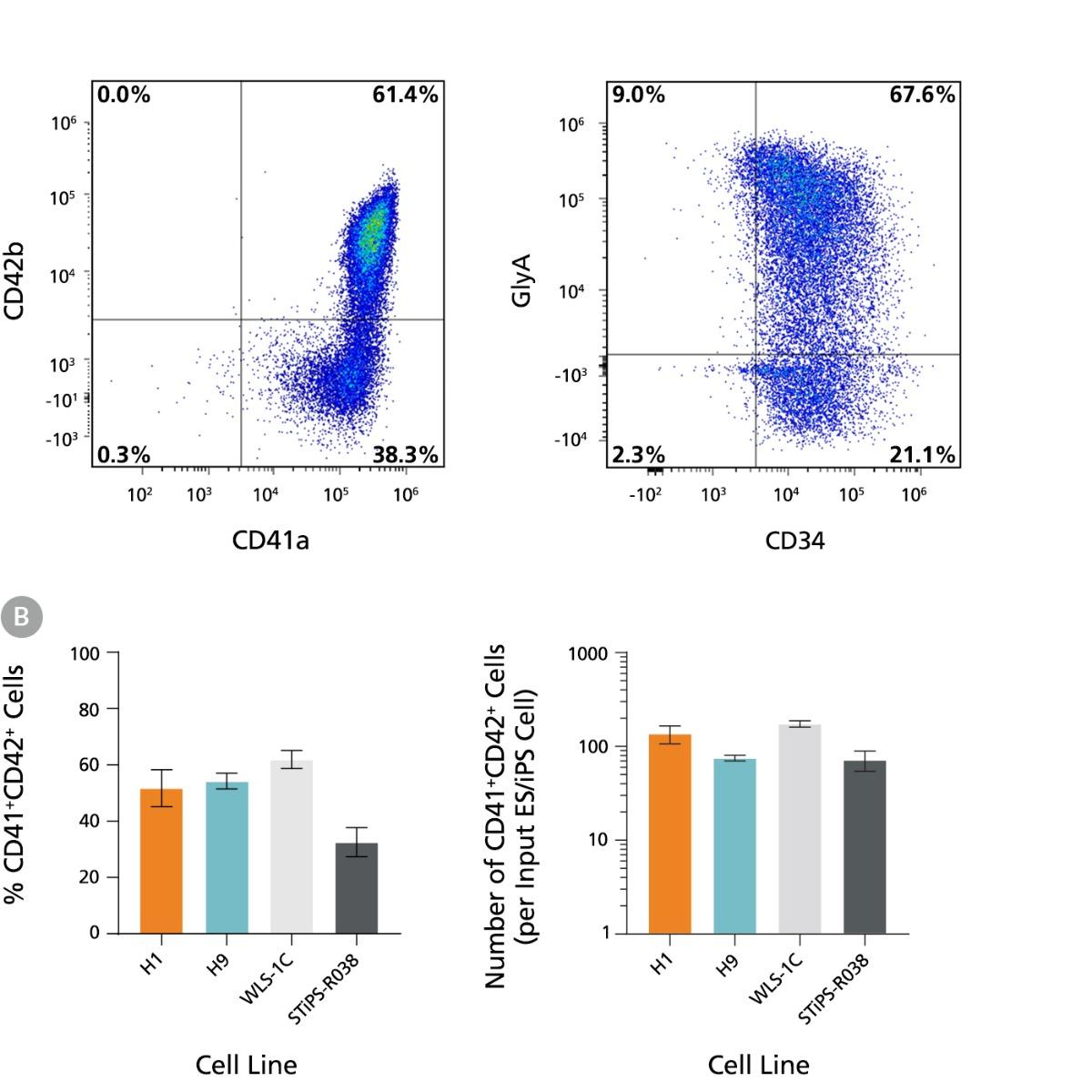
Figure 2. hPSCs Differentiate to Megakaryocyte-Erythroid Progenitors During 12 Days of Culture
hES and hiPS cells were induced to differentiate to megakaryocyte-erythroid biased HPCs following the protocol described in Figure 1. On Day 12, cells were harvested from the supernatant and analyzed for expression of CD41a, CD42b, CD34, and GlyA by flow cytometry. Dead cells were excluded by light scatter profile and propidium iodide (PI) staining. (A) Representative flow cytometry plots for hES-derived (H9) cells on Day 12. The cells show high levels of CD41a and CD42b as well as of CD34 and GlyA expression, indicating that the protocol supports differentiation of hPSCs to megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitors by Day 12. (B) Frequencies and numbers of CD41a+CD42b+ cells per input cell for two hES cell lines (H1 and H9) and two hiPS cell lines (WLS-1C and STiPS-R038). The average frequency of viable CD41a+CD42b+ cells on Day 12 ranged between 33% and 62%. The average yield of CD41a+CD42b+ cells generated per input cell ranged between 72 and 174. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 7 for H1, n = 20 for H9, n = 19 for WLS-1C, n = 7 for STiPS-R038).
Figure 4. hPSC-Derived Megakaryocytes Generated Using STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit Are Polyploid
hPSC-derived MKs obtained using STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit display mature and adult-like features: cellular enlargement and polyploidization. (A) A representative bright-field image taken on Day 17 showing large MKs derived from H1 cells (10X magnification). (B) Representative immunofluorescence images taken on Day 17 showing that CD41a+ MKs derived from H1 and WLS-1C cells are polyploid (20X and 63X magnification, respectively). The cells were formaldehyde-fixed and stained with a fluorescein-conjugated antibody against surface marker CD41a (green), and DAPI (blue). (C) A representative cytospin of MKs derived from H9 cells on Day 17 showing high ploidy (40X magnification, May-Grunwald Giemsa stain). (D) Representative flow cytometry histogram and scatter plot showing the DNA ploidy profile of ethanol-fixed MKs derived from H9 cells on Day 17. The DNA content was determined by the quantity of PI staining, with different peaks on the histogram representing 2N, 4N, and 8N+ cells. Ploidy analysis was done on gated CD41a+ cells. (E) Ploidy distribution of MKs generated from two hES cell lines (H1 and H9) and two hiPS cell lines (WLS-1C and STiPS-R038). The average ploidy distributions of CD41a+ cells on Day 17 were 66%, 24.5%, and 9.5% for 2N, 4N, and 8N+, respectively. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 6 for H1, n = 28 for H9, n = 19 for WLS-1C, n = 10 for STiPS-R038).
Figure 5. hPSC-Derived Megakaryocytes Generated Using STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit Yield Platelet-Like Particles
hPSC-derived MKs obtained using STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit are capable of proplatelet formation to yield functional platelet-like particles (PLPs). (A) A representative bright-field image taken on Day 17 showing MKs derived from H1 cells formed proplatelets, (long cytoplasmic protrusions,10X magnification). (B) Representative flow cytometry forward/side scatter profile of MKs and PLPs and histogram of PLPs derived from H9 cells on Day 17. The PLP gate is based on control platelets (PLTs) prepared from fresh blood. Cells were also stained with antibodies against CD41a, CD45, and GlyA for PLP characterization and enumeration. PLPs showed a high level of CD41a expression (and no CD45 and GlyA expression, data not shown) as in control PLTs. Grey filled histogram represents CD41a Fluorescence Minus One (FMO) control. (C) Numbers of PLPs generated per MK on Day 17 for two hES cell lines (H1 and H9) and two hiPS cell lines (WLS-1C and STiPS-R038). PLPs and MKs were enumerated based on the number of CD41a+CD45-GlyA- cells in the PLP gate and viable CD41a+ cells in the MK gate, respectively. The average yield of PLPs generated per MK ranged between 3.2 and 5.1. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 12 for H1, n = 28 for H9, n = 27 for WLS-1C, n = 12 for STiPS-R038).
Figure 6. STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit Produces More Megakaryocytes and Platelet-Like Particles than Other Published Protocols
hES and hiPS cells were differentiated into MKs using STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit and using four different published protocols from the literature with modifications. (A) Frequencies and numbers of CD41a+CD42b+ MKs per input cell for two hES cell lines (H1 and H9) and two hiPS cell lines (WLS-1C and STiPS-R038) were analyzed by flow cytometry as shown in Figure 2. (B) Numbers of PLPs generated per input cell were enumerated as described in Figure 5. Compared to the published protocols, STEMdiff™ Megakaryocyte Kit produced 10- to 40-fold more CD41a+CD42b+ MKs and 6- to 23-fold more PLPs per input cell. P values were calculated using a one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 7 - 8).